Neat Info About How To Increase Heart Stroke Volume

Stroke volume increases with physical activity because your exercising muscles need more oxygen and nourishment, which are both received from the blood.
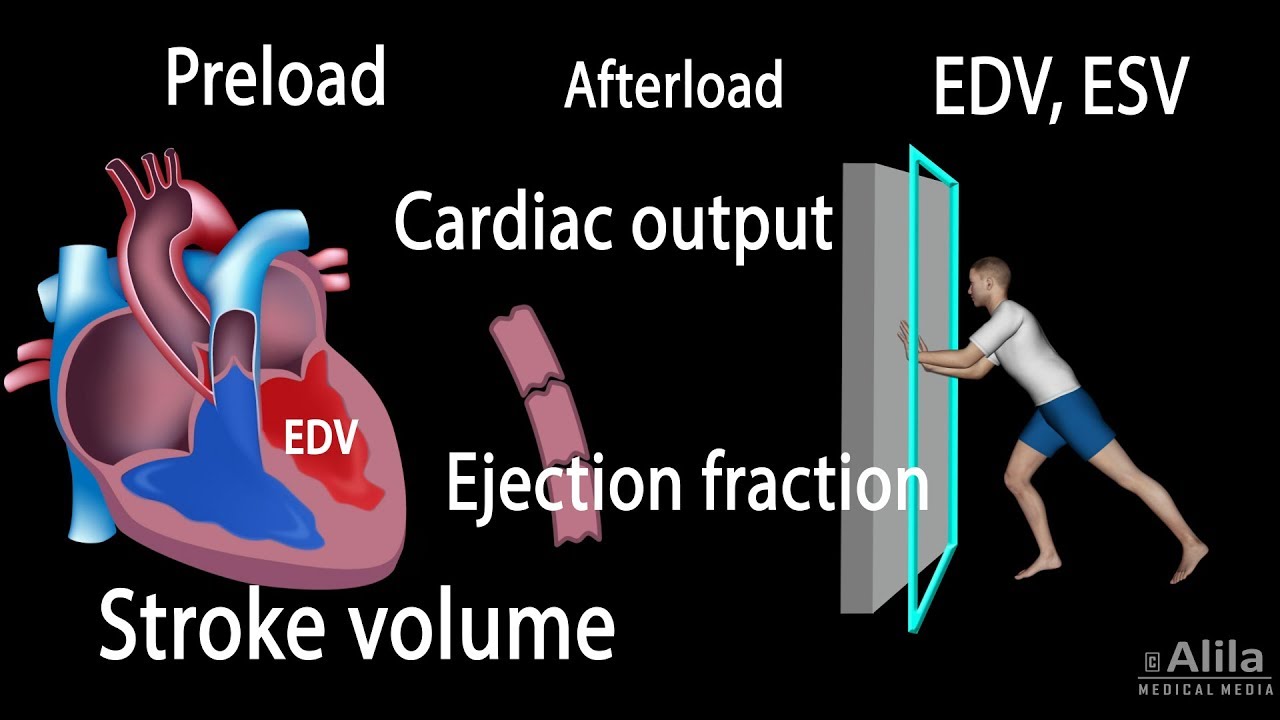
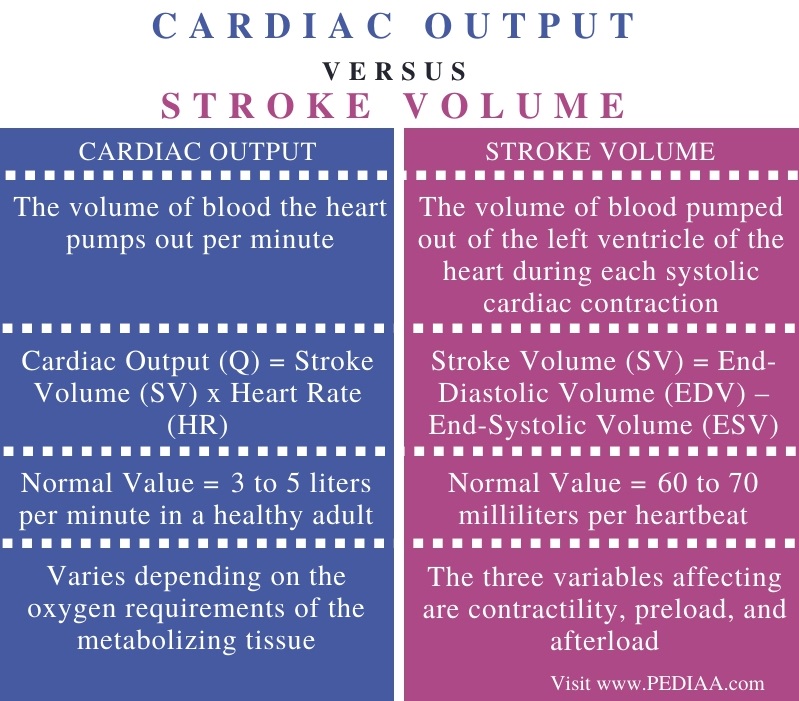
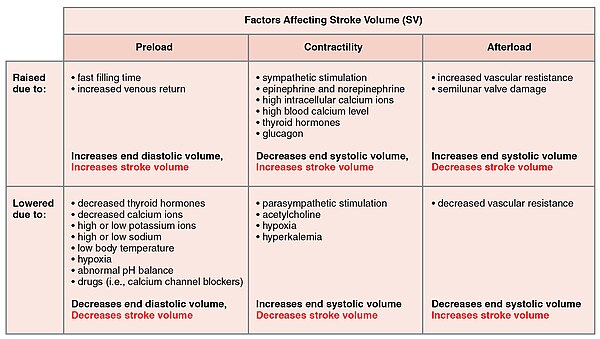
How to increase heart stroke volume. Stroke volume is determined by preload, contractility, and afterload. The most common stroke volume equation is: This may be achieved by an increase in the systolic emptying of the heart as might occur with.
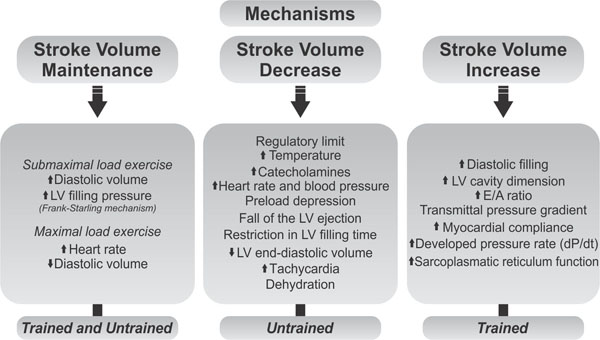
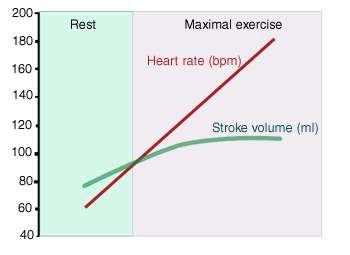
Due to the increased size of the ventricular walls, the heart can increase the size of is ventricular contraction and the athlete’s stroke volume. The normal range for cardiac output is. It does not change as intensity of exercise increases from approximately.
A high capacity oxygen transport system requires a large cardiac stroke volume. The most effective training intensity for increasing stroke volume is one that elicits your vo2max: A 2 × 2 factorial study of changes in heart rate (80 bpm and 110 bpm) and tidal volume (6 ml/kg and 10 ml/kg).
Here’s the equation (where co = cardiac output (liters/min), hr = heart rate (beats/min), and sv = stroke volume (milliliters)): Stroke volume can also be obtained by pulsed. Given this stroke volume and a normal heart rate of 70 beats per minute, cardiac output is 5.25 l/min.
Anxiety and stress can elevate the heart rate, too. An increase in the volume or speed of venous return will. Therefore, the stroke volume is increased.
“exercise is the number one way to lower resting heart rate,” says dr. This, too, increases the cardiac. If your body needs more blood, then your heart will increase the cardiac output.
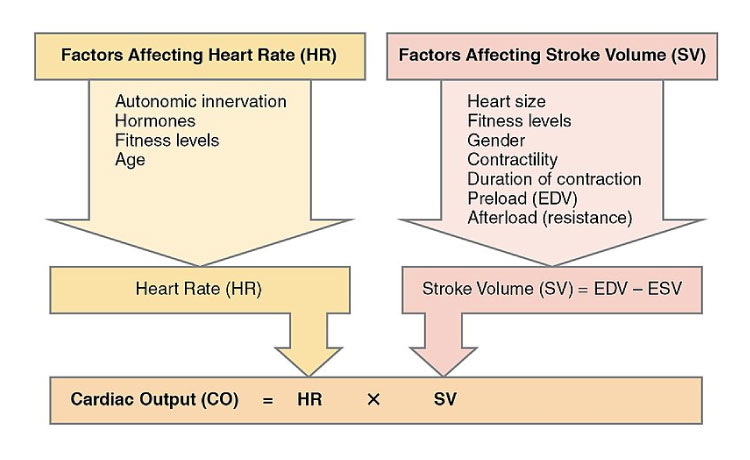
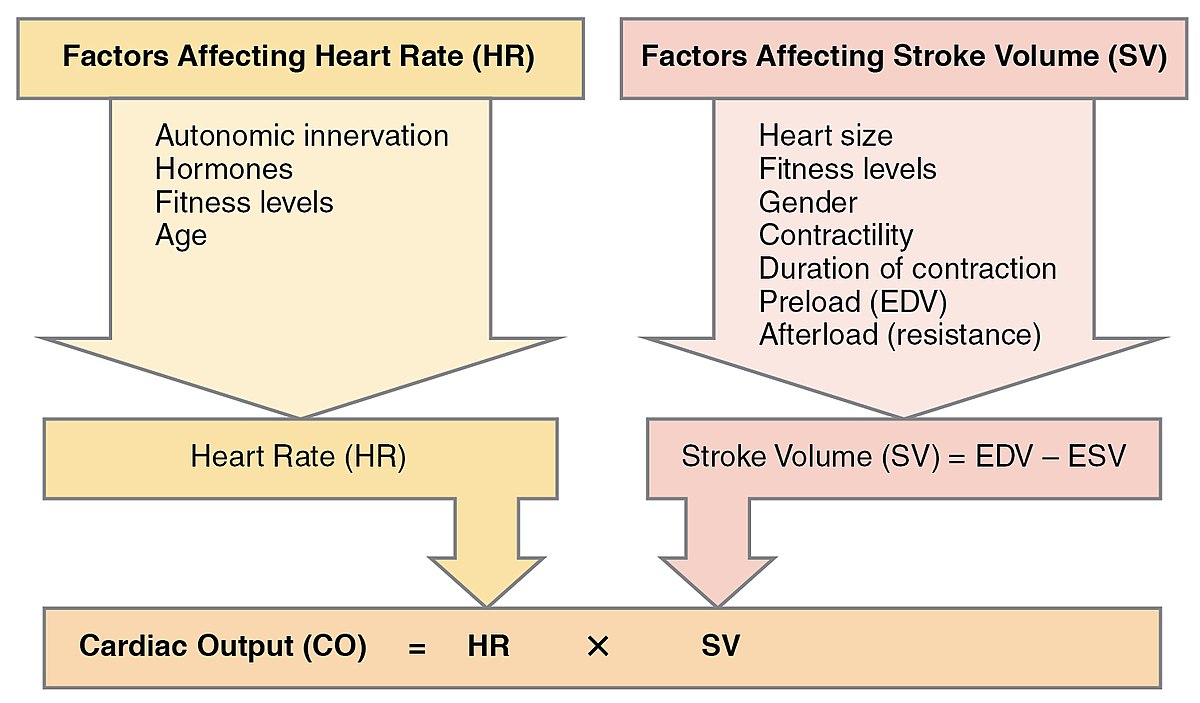
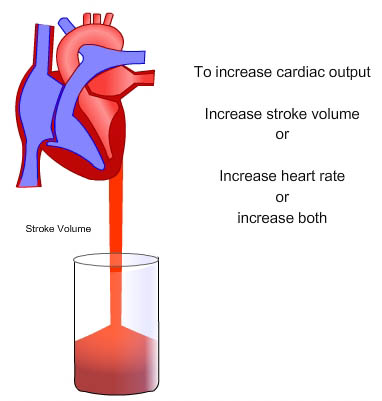
Cardiac output is calculated by multiplying the stroke volume by the heart rate. An increase in stroke volume occurs when there. Improving stroke volume is a key contributor to why heart rate reduces at the same intensity through training & adaptation, but why and how does it improve?
With tidal volume at 6. Stroke volume is intrinsically controlled by preload (the degree to which the ventricles are stretched prior to contracting). Heart rate (beats/min.) x stroke volume (ml) = cardiac output.
There are three proposed mechanisms for how stroke volume increases, which are summed up in the following points: You can calculate cardiac output using stroke volume and heart rate, and you can calculate it in millilitres or litres per minute.